Understanding the Role of Embeddings in RAG LLMs

Understanding RAGs and the Role of Embeddings
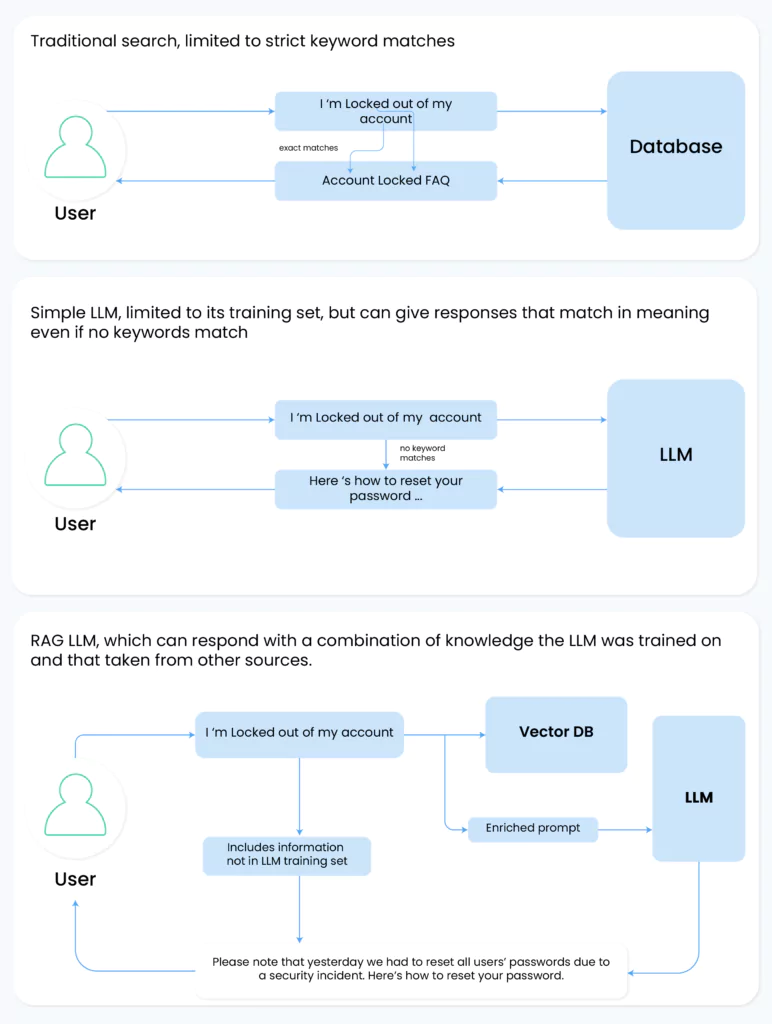
Think about searching for documents in a vast digital library. You’re looking for information on a specific topic. In RAG LLMs, the system does more than just search for text that matches your query.
It actually digs into the deeper context of the documents and finds the information that’s most relevant to your topic. That’s where embeddings come into play. They help the system understand and retrieve the most suitable information for you.
Open Source Large Language Models can be integrated with RAG systems to enhance this capability, offering customizable and efficient solutions for managing large datasets.
Why embeddings over regular text search?
A regular text search, like that performed by Solr, operates on literal text matches. It’s efficient but can miss nuanced or contextually relevant documents that don’t contain exact search terms.
Embeddings, however, represent documents as vectors in a high-dimensional space, capturing semantic relationships beyond mere word presence.
In the context of a large corpus, the challenge is to identify the broadest set of relevant document chunks within the finite context window of an LLM. Embeddings excel here, enabling the system to identify and retrieve content that a literal text search might overlook.
Embedding Types and Chunking Algorithms in RAG LLMs
Embedding types: In the context of RAG LLMs, various types of embeddings can be utilized, such as Word2Vec, GloVe, or BERT embeddings. Each of these has unique characteristics. For instance, Word2Vec captures semantic relationships based on word co-occurrences, while BERT embeddings, derived from transformer models, are contextually richer, capturing the nuances of word meanings based on surrounding text.
Chunking algorithms: The process of breaking down documents into semantically cohesive chunks is pivotal in RAG LLMs. Algorithms like Sentence-BERT can be used to generate embeddings for individual sentences, facilitating the identification of semantically dense chunks. The choice of algorithm significantly influences the granularity and relevance of the information retrieved.
Chunking in vector databases vs. regular search
The process of chunking in vector databases involves segmenting documents into portions that are semantically cohesive, ensuring that each chunk encapsulates a complete idea or concept. This is different from regular text search, where the focus is more on keywords and specific text fragments.
Integrating Embeddings with LLMs
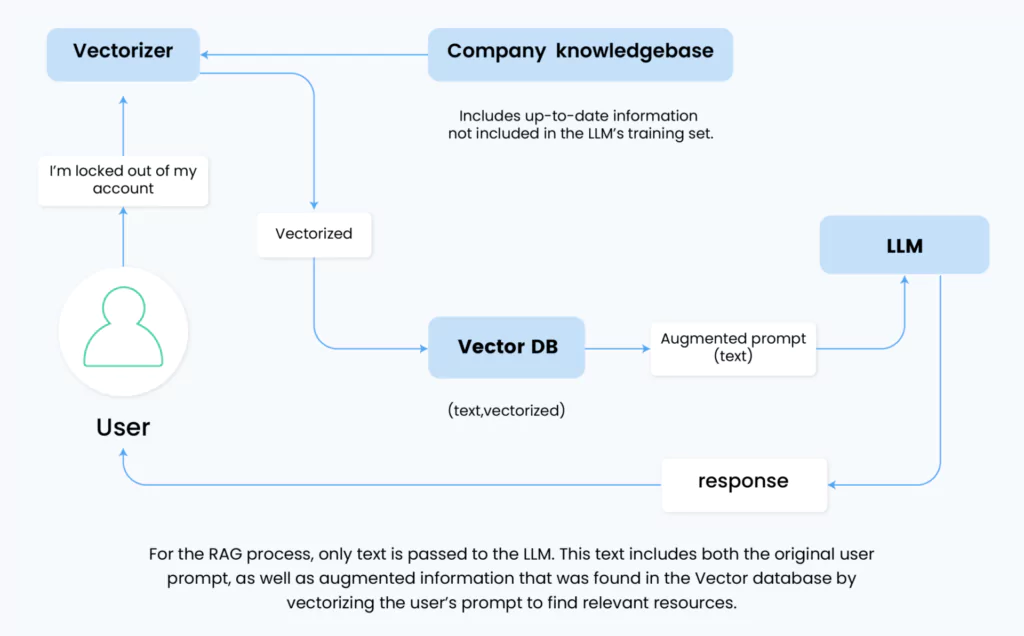
It’s a common misconception that embeddings are directly fed into LLMs as part of the prompt. In reality, embeddings serve as an intermediate step. They guide the retrieval of text chunks from the database, which is then converted back into a readable format and combined with the original user prompt. This enriched prompt is what’s actually fed into the LLM.
The LLM doesn’t process the embeddings directly. Instead, it works with the enriched text, leveraging its own encoding mechanisms to interpret this information.
RAG’s Impact on LLM Architecture
Integrating RAG into an LLM isn’t just a matter of wrapping an existing model in a new layer. In RAG systems that use GPT-4 as the LLM model, the architecture of the LLM itself is not modified. Instead, a vector layer is added in front, augmenting the prompts, which allows the model to handle enriched prompts effectively by interpreting the additional context and integrating it seamlessly with the user’s original query.
The Challenges of Implementing RAGs
RAG systems are inherently complex due to several factors:
- Context window limitations: The challenge is to find the most relevant information within the constraints of the LLM’s context window.
- Relevance search: Identifying the most pertinent document chunks is a nuanced task, involving more than just finding literal text matches.
- Chunking strategies: Different approaches to breaking down documents into manageable chunks can impact the accuracy and relevance of the search results.
Conclusion
In summary, embeddings play a crucial role in RAG LLMs, enabling a more nuanced and contextually rich retrieval of information. The integration of embeddings into LLMs is not just a matter of compression or skipping steps in processing; it’s about enhancing the model’s ability to comprehend and respond to complex queries. Implementing RAG involves architectural adjustments to the LLM and a deep understanding of the challenges associated with relevance search, context window limitations, and effective chunking strategies.
Feel free to reach out to us with any questions.




