SIEM Tools: Key Capabilities and 8 Tools You Should Know

Key Features of SIEM Solutions
Data Aggregation
SIEM tools collect security events and logs from diverse sources across an organization’s IT infrastructure. By consolidating this data into a centralized platform, SIEM tools provide security analysts with a holistic view of the organization’s security landscape.
Data aggregation enables organizations to identify patterns and trends, helping them understand the overall security posture and detect potential threats. SIEM tools leverage various data collection methods, including log collectors, agents, and APIs, to ensure comprehensive coverage of security events.
Threat Intelligence
SIEM tools integrate threat intelligence feeds to enhance their threat detection capabilities. These feeds provide up-to-date information about known threats, vulnerabilities, and indicators of compromise. By incorporating this threat intelligence into their analysis, they can identify and prioritize potential security incidents more effectively.
Threat intelligence feeds enable SIEM tools to correlate security events with known attack patterns, signatures, and indicators of compromise. This proactive approach helps organizations stay one step ahead of cybercriminals by quickly detecting and mitigating potential threats.
Correlation, Security Monitoring, and Alerts
SIEM tools excel at correlating security events from different sources to identify meaningful patterns and potential threats. By analyzing the relationships between various security events, SIEM tools can identify complex attack scenarios that may span multiple systems or timeframes.
Security monitoring is another critical feature of SIEM tools. These tools continuously monitor security events in real-time, allowing organizations to respond swiftly to potential threats. SIEM tools generate alerts based on predefined rules and thresholds, enabling security analysts to focus on critical security incidents.
Advanced Analytics
Advanced analytics is a crucial feature of modern SIEM tools. These tools employ various techniques, such as machine learning and behavior analytics, to identify abnormal activities and potential security breaches. By applying advanced algorithms to security event data, SIEM tools can detect subtle patterns and anomalies that may go unnoticed by traditional security solutions.
Advanced analytics capabilities enable SIEM tools to establish baselines of normal behavior for users, devices, and applications. Any deviations from these baselines can trigger alerts, indicating potential security incidents. By continuously learning from security events, SIEM tools improve their detection accuracy over time.
Forensic Analysis
SIEM tools provide forensic analysis capabilities that assist organizations in investigating security incidents. In the event of a breach, SIEM tools offer detailed logs and historical data that can be used to understand the attack timeline and identify the root cause.
Forensic analysis features enable security analysts to conduct deep dives into security incidents, gathering evidence and extracting actionable intelligence. This information is vital for organizations to close security gaps, remediate vulnerabilities, and improve their overall security posture.
Popular SIEM Security Tools
1. Coralogix
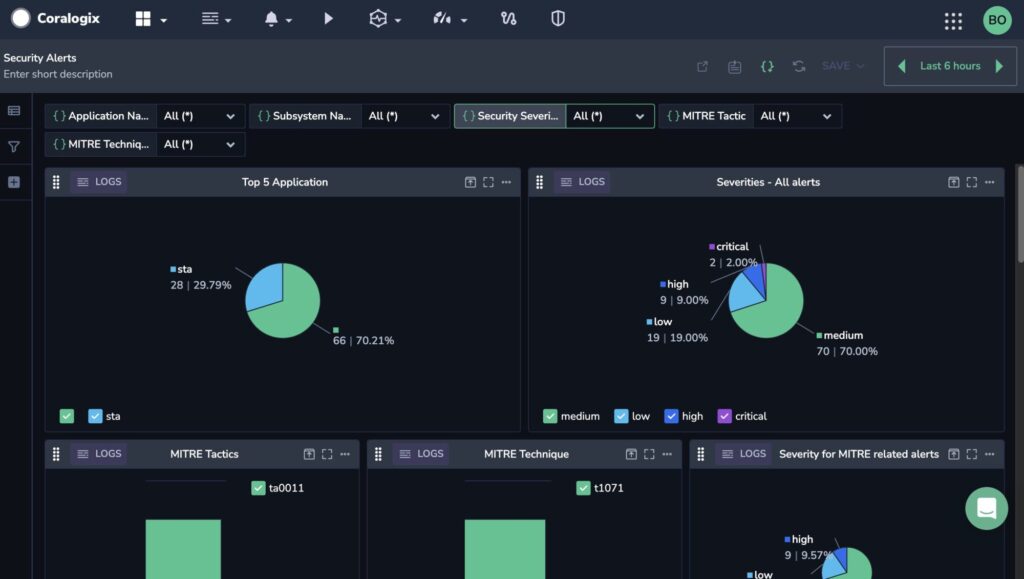
Part of Coralogix’s full-stack observability platform includes a SIEM offering, giving users end-to-end protection.
Users can ingest their security logs, transforming them into actionable insights with hundreds of out-of-the-box integrations and quick start packages that automatically parse logs, generate critical alerts and populate relevant, pre-configured dashboards. Coralogix leverages machine learning capabilities to update alerts, IP blacklists, threat signatures, and other components automatically. Users can streamline their response by integrating security management tools, ensuring end-to-end forensic capabilities.
Coralogix also provides managed detection and response with a highly experienced team of cyber analysts.
Learn more about the Coralogix security offering.
2. Splunk

Splunk’s SIEM solution caters to both security and broader IT operational needs. Its real-time data processing and user-friendly interface make it a popular choice.
However, its limited behavioral analytics and automation, alongside the need for significant customization and challenges in product integration, particularly in detecting advanced threats like lateral movement, are notable drawbacks. Users often report the necessity for specialized skills to effectively utilize its full potential, especially in managing false positives and custom query requirements.
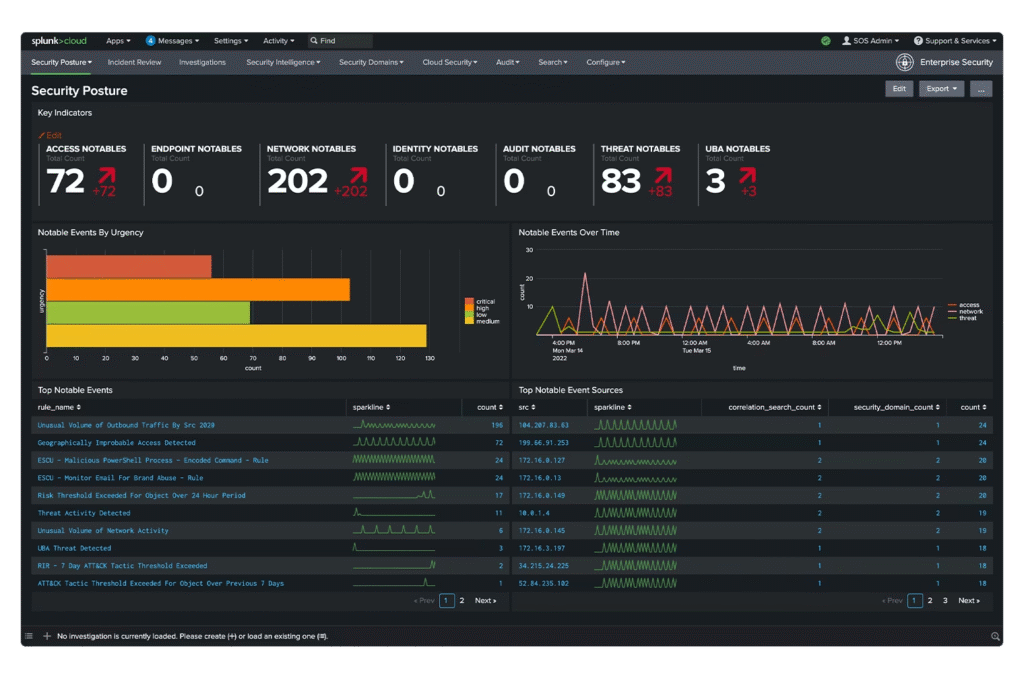
Source: Splunk
3. LogRhythm

LogRhythm stands out in the SIEM landscape with its comprehensive analytical tools, AI integration, and log correlation capabilities.
However, its user interface is considered less intuitive compared to its peers, posing a steeper learning curve. Additionally, LogRhythm’s dependency on IOCs and limited automated detection capabilities, particularly for lateral movement, highlight potential gaps in addressing advanced cyber threats. These aspects, combined with noted deficiencies in cloud-based offerings, present challenges in fully leveraging its analytical strengths.
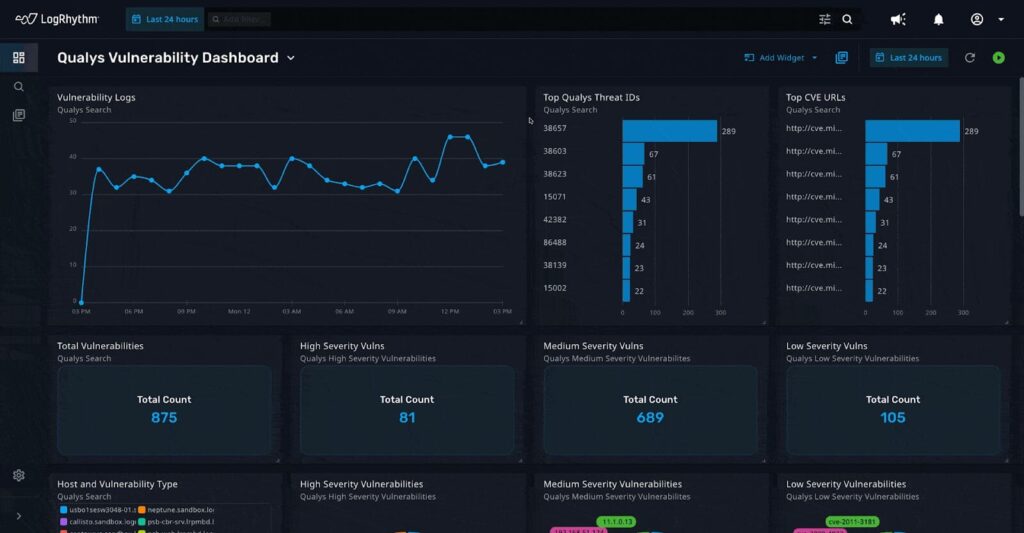
Source: LogRhythm
4. IBM QRadar SIEM

IBM QRadar SIEM is renowned for its real-time visibility and modular architecture, supporting a wide range of logging protocols. It offers substantial analytics and configuration options, complemented by an extensive app store.
However, the solution is not without challenges, including a complex and costly pricing model, and the need for improved collaborative features. Its weak UEBA capabilities and the complexity of upgrades in distributed environments, along with limited product support and reporting capabilities, can hinder its effectiveness in some scenarios.
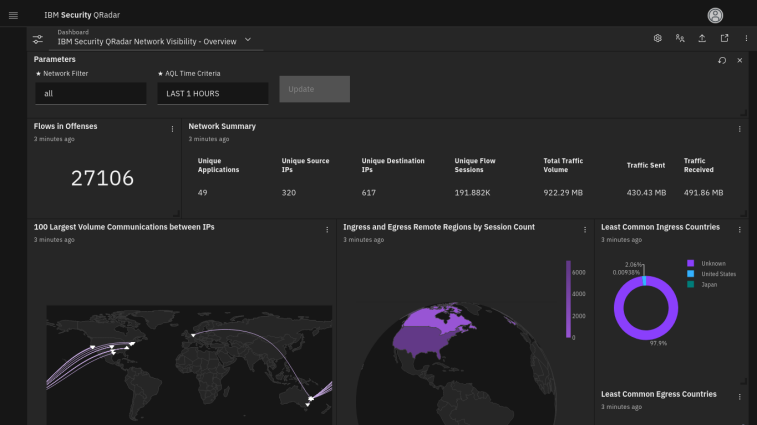
Source: IBM
5. OpenSearch

OpenSearch Security Analytics is a SIEM solution that is part of the OpenSearch Project, a popular open source search and analytics suite. Designed to address various cybersecurity threats, this tool detects, analyzes, and responds to incidents that could compromise business operations.
However, users of OpenSearch might encounter difficulties with the scalability and performance of the tool, particularly in large or complex environments. Managing and maintaining the open-source nature of the project can be challenging, requiring substantial technical expertise.
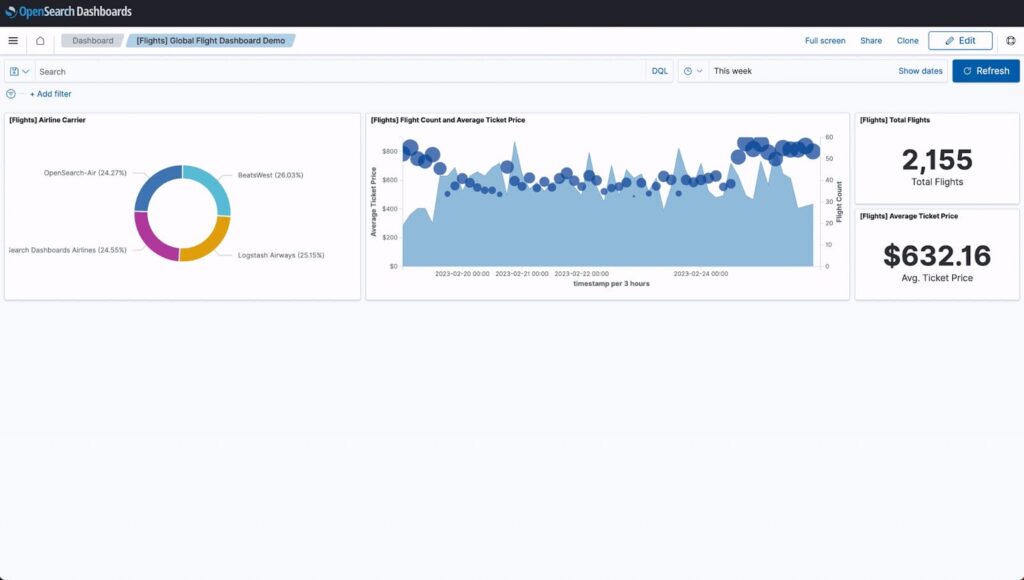
Source: OpenSearch
6. Elastic Stack
The Elastic Stack, also known as ELK stack, offers a suite of open-source tools for application management and monitoring. Its components, including Elasticsearch for log searching, Logstash for real-time log generation, and Kibana for data visualization, provide a powerful toolkit for IT issues detection and security management, which also offers SIEM capabilities.
However, the complexity in setup and management, alongside challenges in third-party tool integration and documentation, present a steep learning curve, making it less accessible for those without technical expertise.
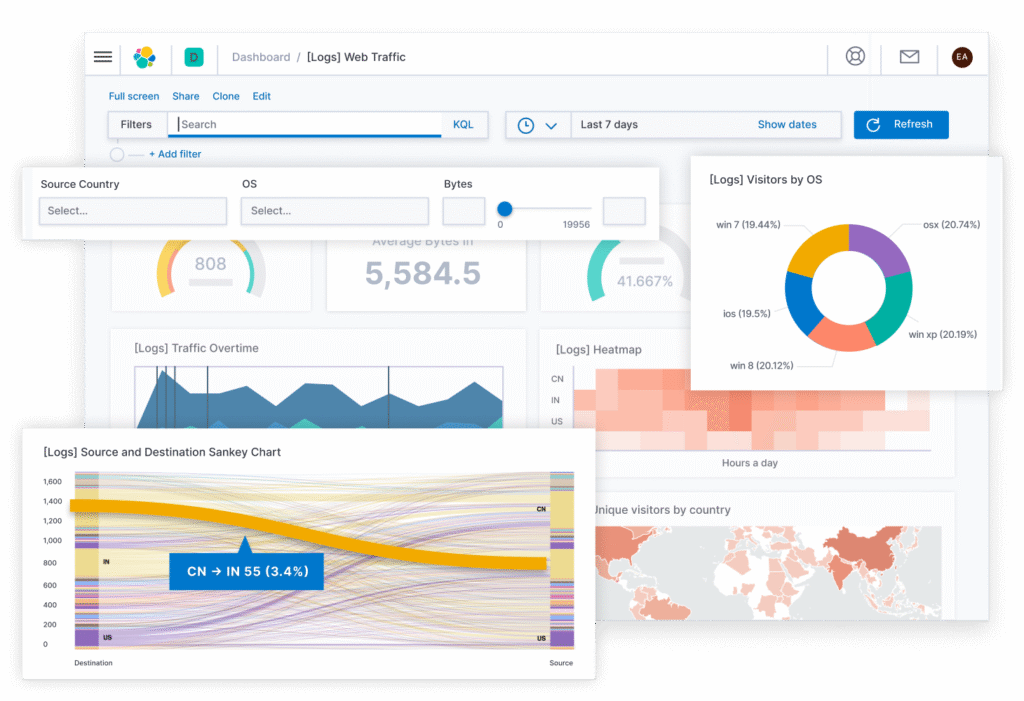
Source: Elastic
7. Exabeam Fusion

Exabeam Fusion, a cloud-delivered SIEM solution, takes a behavior-based approach for efficient threat detection, investigation, and response. It provides an integrated security orchestration, automation and response (SOAR) solution for automated response, as well as scalable cloud-based log storage and comprehensive search and reporting capabilities.
However, users report that the solution can be resource-intensive, requiring significant computing power for optimal performance. Integration with legacy systems and diverse data sources can require additional configuration.
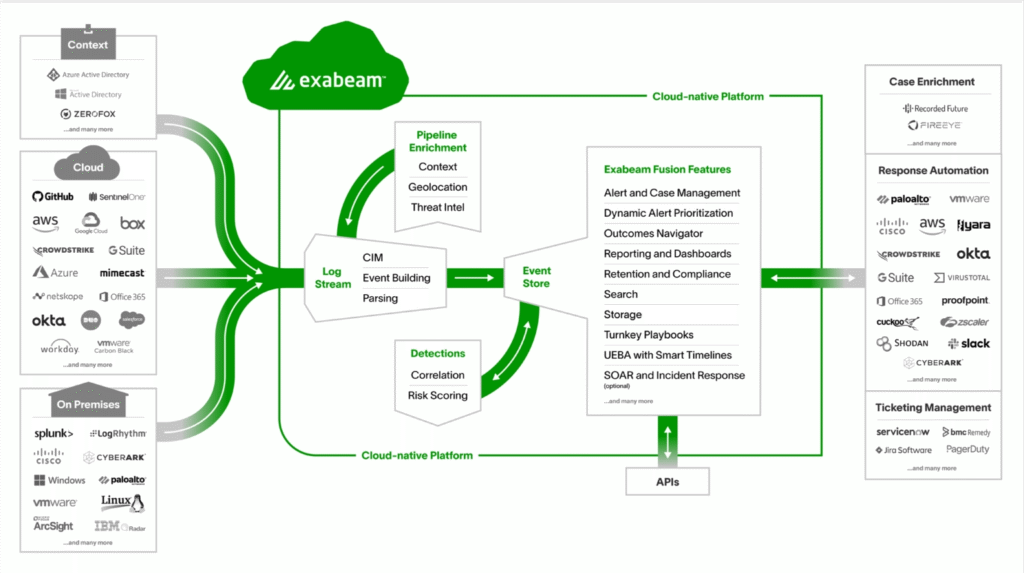
Source: Exabeam
8. Securonix

Securonix is a SIEM solution that provides threat detection, investigation, and response (TDIR) and is based on Snowflake’s Data Cloud. It includes an analytics-driven UEBA engine, and offers a range of vertical-specific offerings offered as Premium Apps within the solution.
However, the solution does not provide a fully developed native SOAR engine and has smaller hot storage in standard packages compared to competitors.
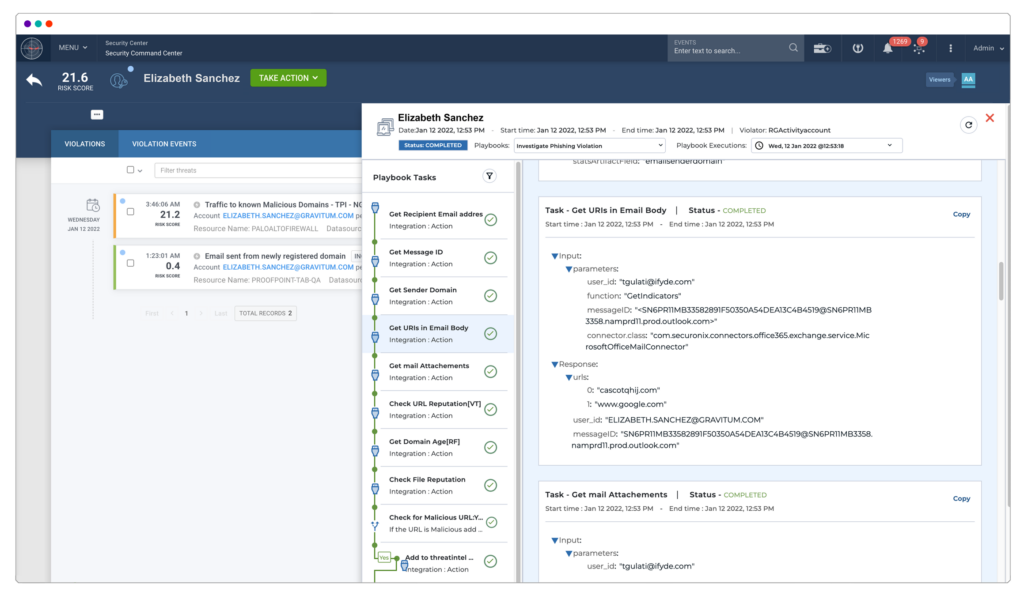
Source: Securonix
Conclusion
In summary, SIEM tools are indispensable in the modern cybersecurity landscape, offering comprehensive solutions for monitoring, analyzing, and responding to security threats. Each tool presents unique features tailored to different organizational needs, including data aggregation, threat intelligence, advanced analytics, and forensic analysis capabilities.
The right SIEM solution, when selected and implemented effectively, can significantly enhance an organization’s ability to detect and respond to cyber threats, thereby strengthening its overall security posture. As the cybersecurity landscape evolves, so too will these tools, continually adapting to meet the emerging threats and complexities of digital security.




