Optimize your CI/CD Pipeline with Coralogix Tagging

Continuous Integration/Continuous Delivery (CI/CD) has now become the de-facto standard for all engineering teams seeking to keep pace with the demands of the modern economy. At Coralogix, we operate some of the most advanced build and deploy pipelines in the world. We’ve baked that knowledge into our platform with a CI/CD Observability feature called Coralogix Tagging.
What is Coralogix Tagging?
The Tagging UI allows Coralogix users to view the delta between events in their system instantly. A Coralogix Tag can be made for anything. Some of our users create tags for an outage, a feature release, or the deployment of new technology. Tags are how Coralogix customers tell the platform that something significant has happened.
How do users explore their Tags?
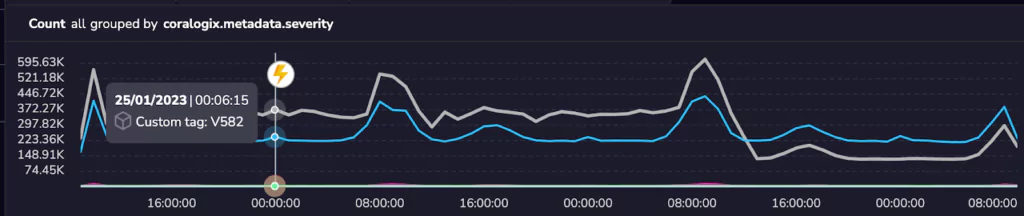
Coralogix Tags appear in several places on the Coralogix platform. Firstly, users can inspect their tags using the Tagging UI. This interface will provide the most information about the difference between two tags.
Moreover, tags also appear on some of our key timeline graphs, especially on the explore screen. This is important because it allows our users to correlate the time a given tag was created with a sudden change in the flow of their logs or a spike in the value of one of their metrics.
What’s in a Coralogix Tag?
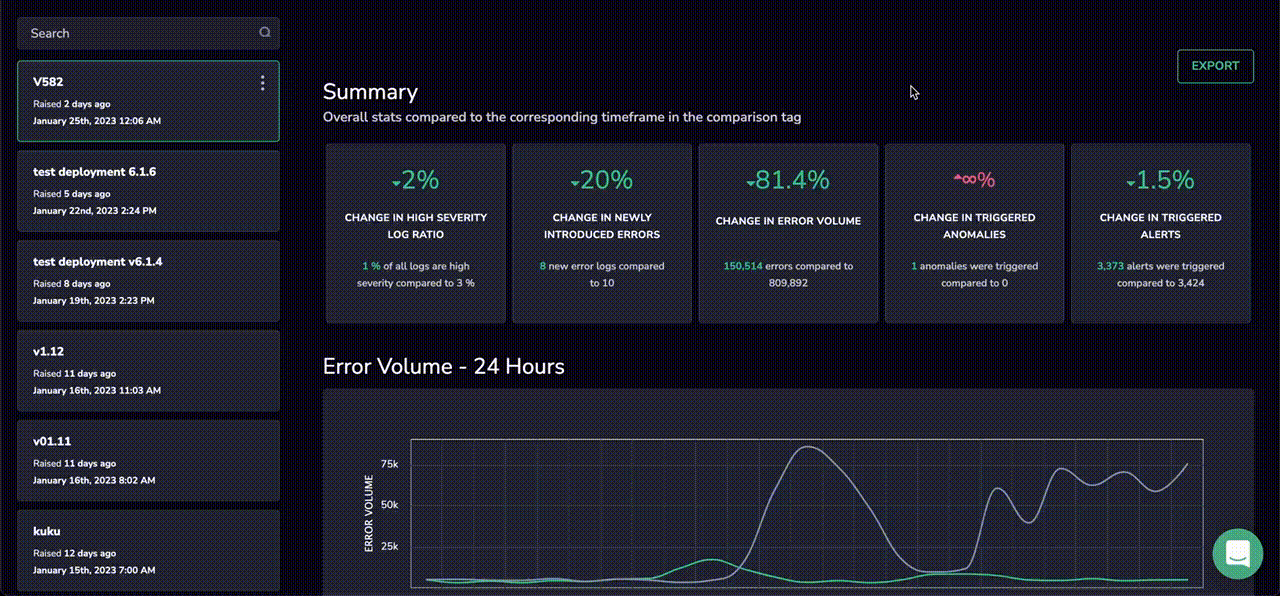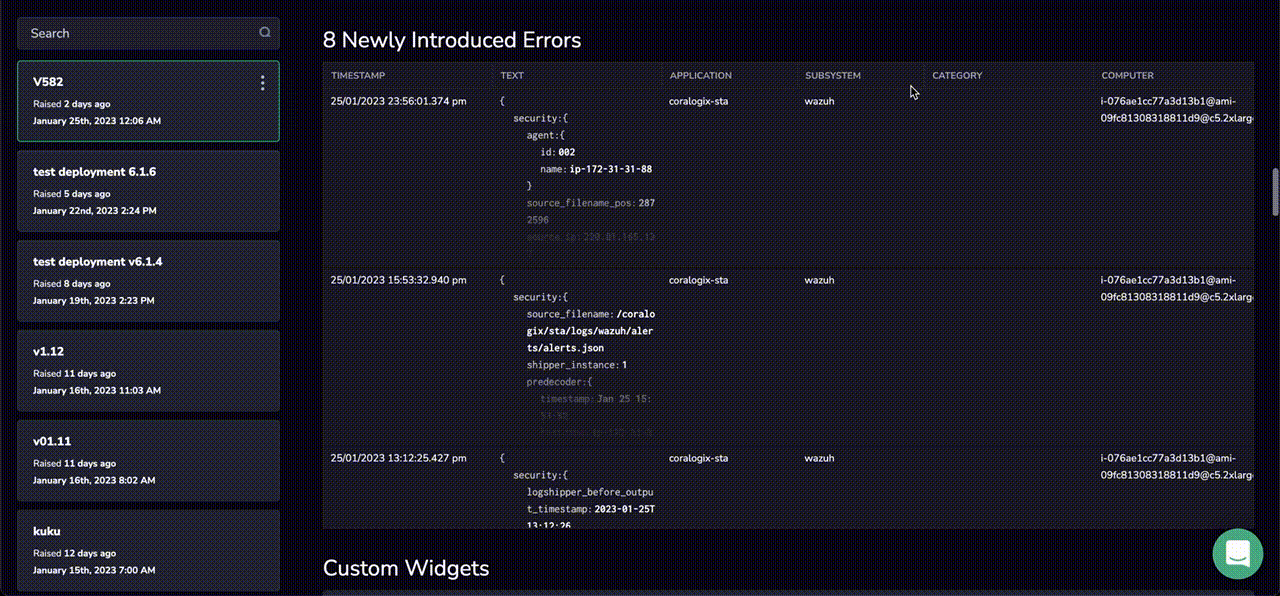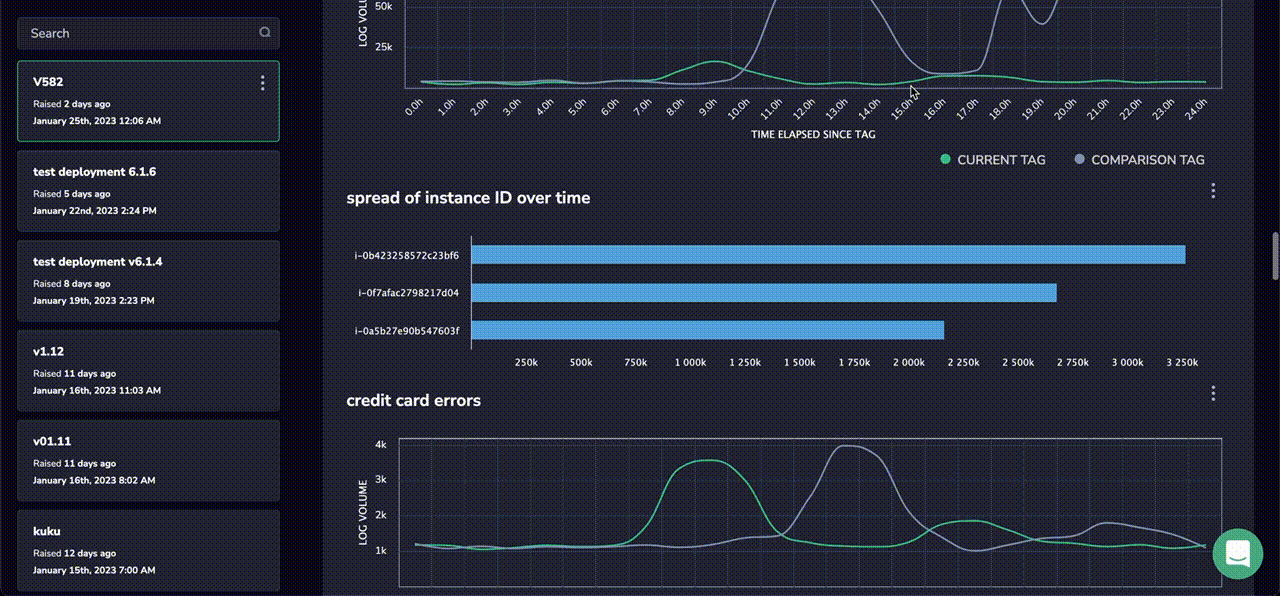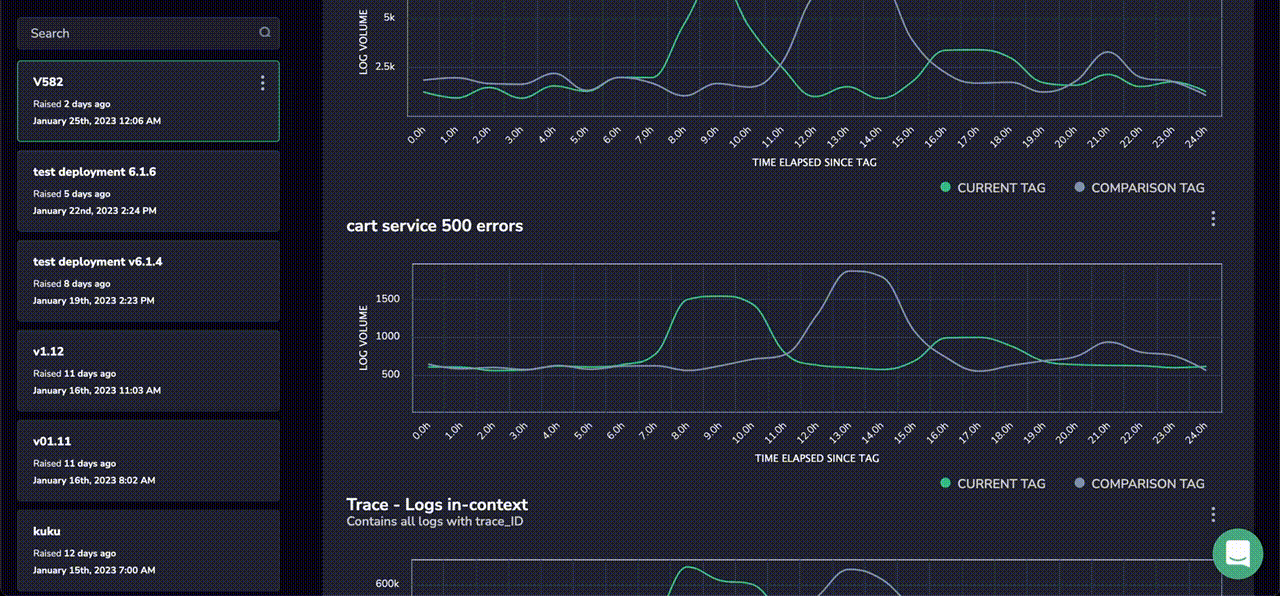
Coralogix Tags represent one of the market’s most advanced error detection systems by providing a collection of metrics in a single, customizable report that can give immediate insight into a system’s health after any event.
The Coralogix Tagging UI begins with a summary section. This section gives Coralogix users the highlights of their most recent release, including a change in the number of error logs and the change in the number of triggered alerts.
Adaptive and Insightful
The interface does not assume that the previous error or alert counts. Instead, it deals with the reality of modern software engineering at scale. A baseline number of errors is tolerable in most systems, and the Coralogix Tagging UI factors this into its reporting. That’s why it uses percentage differences because this is the most pertinent information to give an engineer who has recently released a new version.
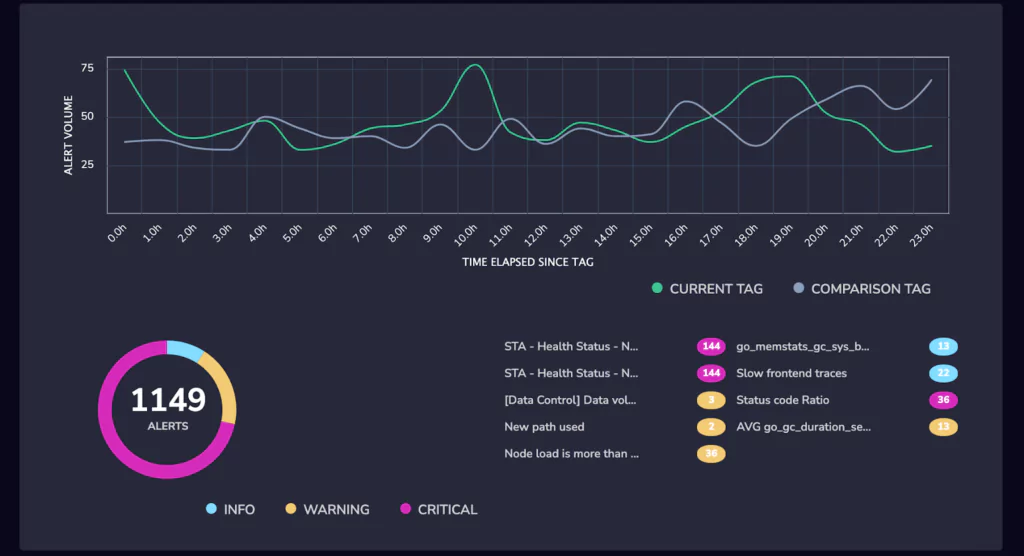
From here, the Tagging UI summarizes the most significant details. It displays all of the triggered alarms, grouped by count, and shows how their volume has changed over time.
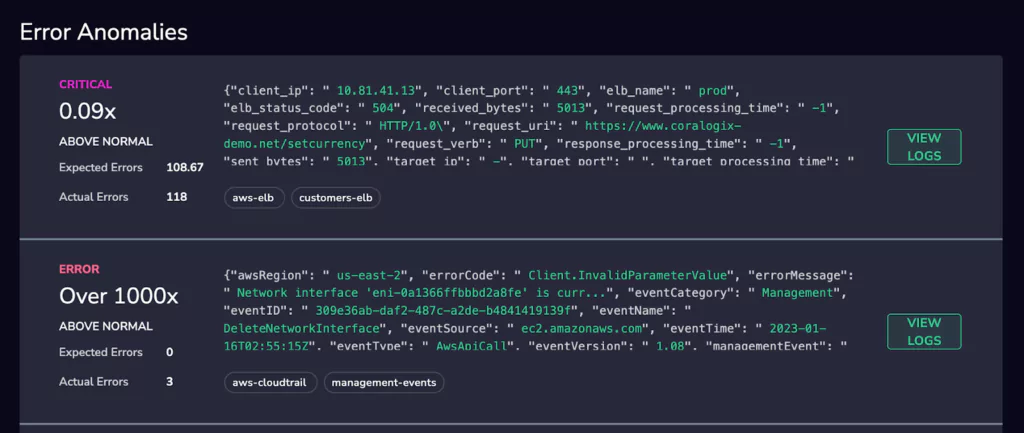
Machine Learning and Anomaly Detection
Coralogix Tagging comes with in-built anomaly detection. The interface will automatically demonstrate when there was an unexpected increase in the flow of Critical & Error logs, following the creation of a Coralogix Tag. This presents information to users that would otherwise be quite tricky to obtain and can give insights into issues that alerts might not cover.
Convenient, but Still Extensible With Custom Widgets
Finally, Coralogix Tagging allows users to define their own custom widgets, meaning that while the report comes with a robust collection of pre-built measures, it can still be tailored to match the specific needs of any organization.
What does Coralogix Tagging do for CI/CD Observability?
The important bottleneck in a CI/CD process is the requirement for a human to ensure that a release has been successful. While automated tests can cover a lot of failure scenarios, organizations still depend on their best engineers to spend time digging into various systems to make sure that their latest release hasn’t had any unintended side effects.
In many organizations, this has constrained their ability to deliver quickly. The pipelines are fast, the automated tests are efficient and thorough, and the product development lifecycle is very lean. Still, this process of hypercare after a deployment has become a problem for the industry. This is a problem that Coralogix Tagging instantly alleviates.




